Forecast for the Salt Lake Area Mountains

Issued by Nikki Champion on
Thursday morning, February 24, 2022
Thursday morning, February 24, 2022
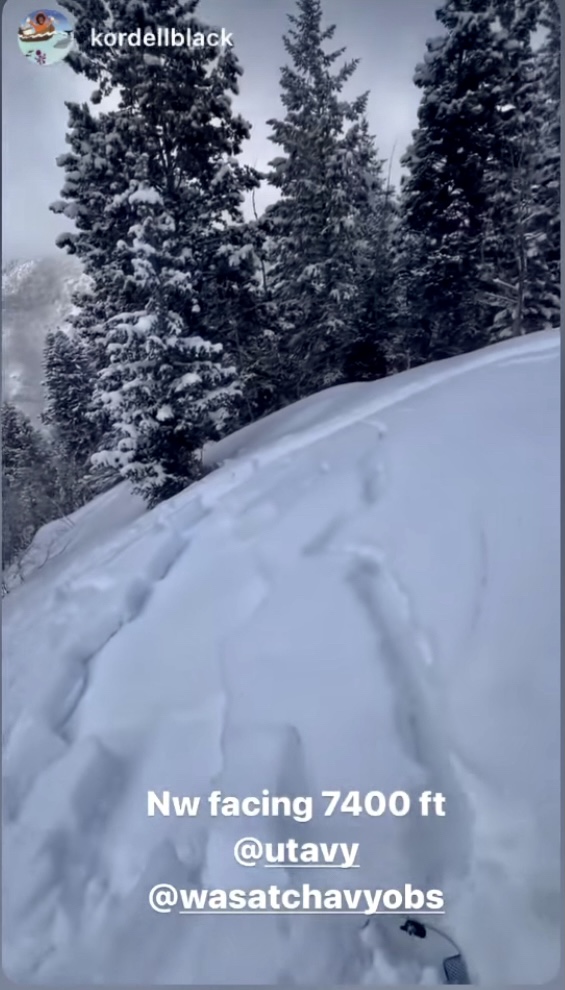
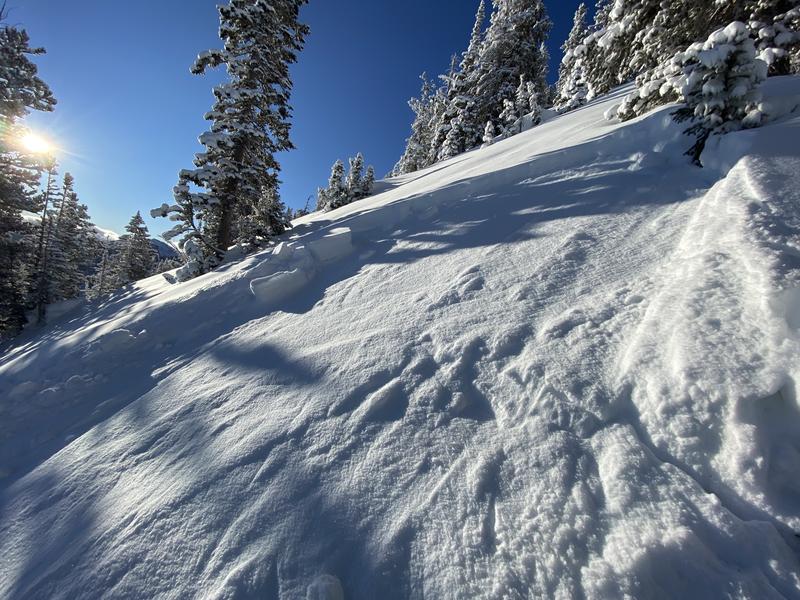
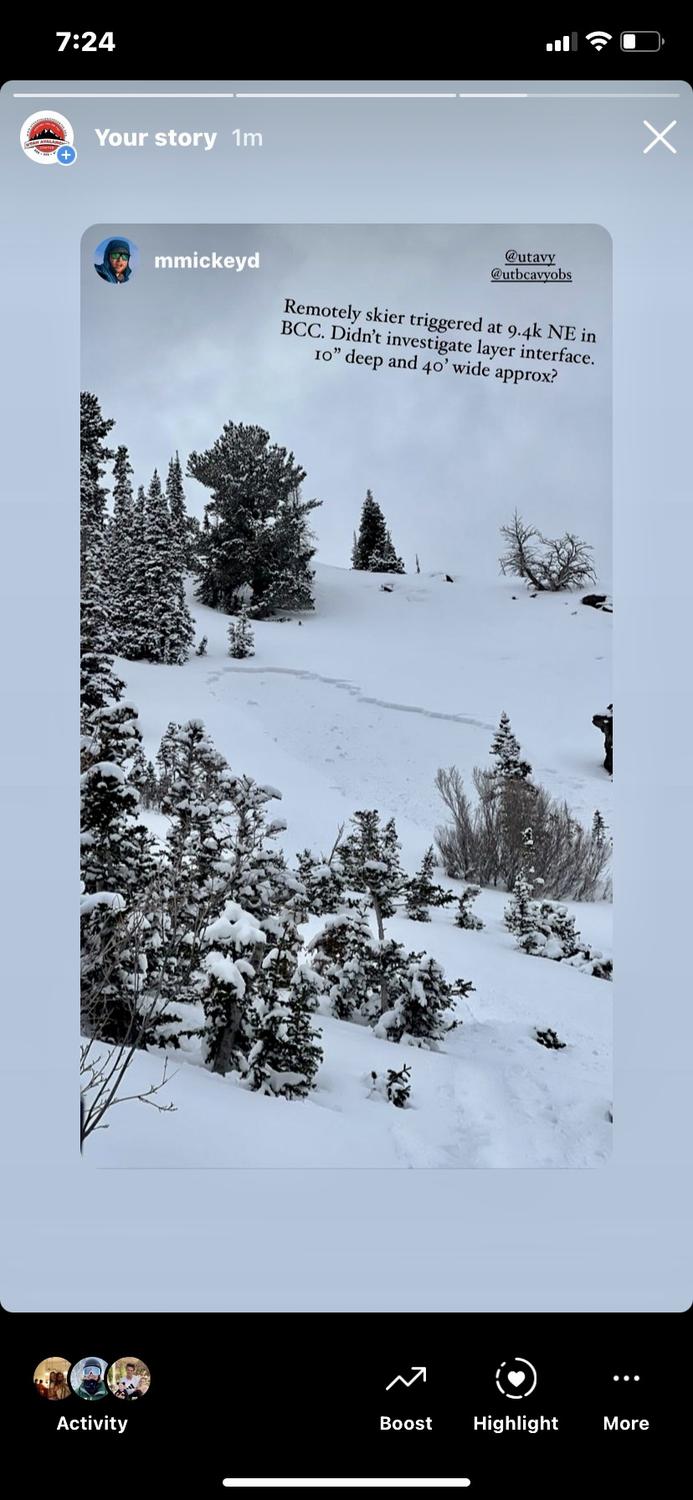
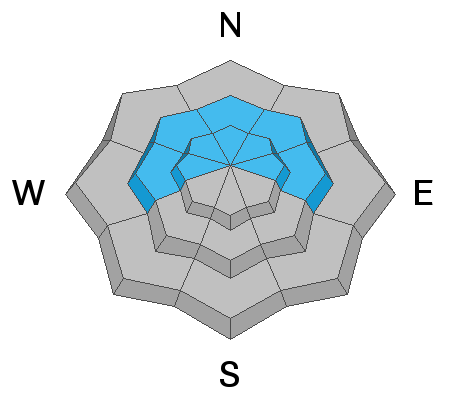
Today, we have a CONSIDERABLE avalanche danger on all steep mid and upper elevation slopes facing west through north through east where fresh wind drifts and new snow sit atop of the weak faceted snow. These types of avalanches are what we call unmanageable as you can trigger them from a distance. These are prime accident conditions.
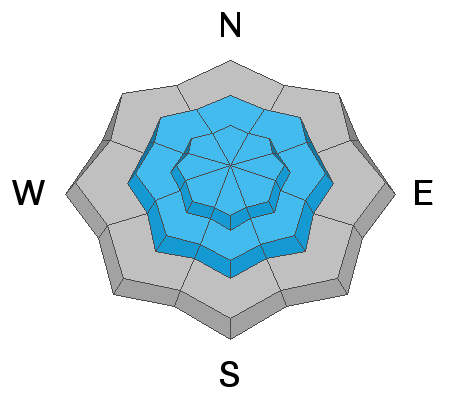
A MODERATE danger exists for all other freshly wind-loaded slopes.
The remaining aspects and elevations have a LOW danger.

Low
Moderate
Considerable
High
Extreme
Learn how to read the forecast here